soil permeability test calculation|permeability of soils chart : wholesaler A good knowledge of soil permeability is needed for estimating the quantity of seepage under dams and dewatering to facilitate underground construction. Soil permeability, also termed hydraulic conductivity, is measured using several methods that include constant .
webJoker - assistir online: streaming, compre ou alugue. Você pode assistir "Coringa" no HBO Max, NOW, Oi Play legalmente online, no Microsoft .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web3 de jan. de 2022 · STHER- Eros guia Área para informações sobre acompanhantes ou casas relatadas ou não no fórum. Antes de enviar mensagem, faça pesquisa a fim de verificar existência de informações.
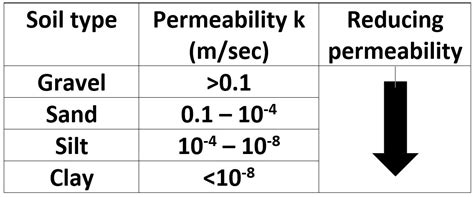
typical permeability values of soil
This calculator determines the coefficient of permeability of a soil using falling head method. The rate of flow under laminar flow conditions through a unit cross sectional are of porous medium under unit hydraulic gradient is defined as .Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.2-2001; ASTM D5856) works the best.This calculator determines the coefficient of permeability of a soil using constant head method. The rate of flow under laminar flow conditions through a unit cross sectional are of porous medium under unit hydraulic gradient is defined as .Soil permeability can be estimated using empirical methods like soil survey mapping, soil texture, or particle size distribution. However, a variety of different laboratory and field test methods make it just as easy to measure these .
The permeability of a soil is the capacity of the soil to allow water to pass through it. Soil permeability is usually represented by the coefficient of permeability (k), where k is the rate of flow of water per unit area of soil when . A good knowledge of soil permeability is needed for estimating the quantity of seepage under dams and dewatering to facilitate underground construction. Soil permeability, also termed hydraulic conductivity, is measured using several methods that include constant . The basic formula for soil permeability, also derived from Darcy’s Law, is: q=k⋅A⋅ΔhLq = k \cdot A \cdot \frac {\Delta h} {L}q=k⋅A⋅LΔh. Where: q is the discharge or flow rate (volume per time, such as m³/s). k is the .
Standard Test Method for Permeability of Granular Soils (Constant Head) Abstract. This test method covers the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils.The calculation takes into account the size of the sample, the cross-sectional area of the standpipe, as well as the time it took to change the water level. . Soil Permeability Testing Equipment: Permeability Cells (Flexible-Wall): Humboldt's HM-4188B Permeability Cells and our HM-4199B Triaxial Cells can be used to measure hydraulic .FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is defined Simple Field Percolation Test – measuring the rate of drop in water level in an accurately sized hole enables calculation of saturated soil conductivity, an indicator of soil permeability. Field tests often provide more .
Purpose Permeability is one of the primary concerns in geotechnical engineering research. The permeability coefficient, the most significant parameter defining permeability, has a significant impact on the mechanical and physical properties of the soil by virtue of its value. Because soil is a bulk material and its internal seepage channels are intricate, it is challenging .Permeability of soils is required in solving pumping seepage water from construction excavations. The stability of slopes and retaining walls can be greatly affected by the permeability of the soils Permeability influences the rate of settlement of a saturated soil under load. The following applications illustrate the importance of The testing and calculation procedure for granular soil permeability determination are presented. Scope. 1.1 This test method covers the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils. The procedure is to establish representative values of the coefficient of .
What is the ASTM test for permeability of soil? The ASTM test for soil permeability is the D 2434 Standard Test Method. This method determines the coefficient of permeability. It involves metal rings filled with water and two Mariotte tube devices to maintain a constant liquid level. Related Blogs. The Essential Guide to Concrete Tests5.3 The linearity (of Darcy’s law) between the hydraulic gradient and the average velocity of flow the soil under test should be established by performing the test over a range of hydraulic gradients. Any deviation from linearity observed should be noted. 5.4 Record of Observations : Where, K27 = Permeability at 27°C KT = Permeability at T°C
Methods of testing soils for engineering purposes Soil classification tests . Soil classification tests, Calculation of the cone plasticity index of a soil. Google Scholar. Australian Standard (AS 1289.3.6.2). 1995. . Determination of permeability of a soil-Constant head method using a flexible wall permeameter. Google Scholar.
Surface tests like infiltrometers suit field permeability testing of pavement bases and landscaping soils. Overview of ASTM Standards for Measuring Soil Permeability. Key standards framing consistent permeability test methodology include: ASTM D2434 constant head lab method; ASTM D5084 flexible wall permeameter cells
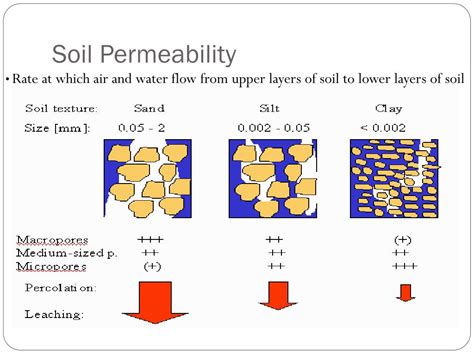
The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils. A separate constant head method for granular soils has been recommended by Indian Standards (IS: 2720 – Part 36, 1975).
This appendix provides background to methods of estimating permeability of soil by correlation with particle size distribution (PSD) analyses. Methods of obtaining soil samples and the subsequent laboratory testing processes are presented briefly, and some potential limitations with the correlation methods are discussed. . Calculation and . Capillarity-Permeability Test: The set-up for the test essentially consists of a transparent tube about 40 mm in diameter and 0.35 m to 0.5 m long in which dry soil sample is placed at desired density and water is allowed to flow from one end under a constant head, and the other end is exposed to atmosphere through air vent.The coefficient of permeability varies with the void ratio as e/sup>/(1+e). For a given soil, the greater the void ratio, the higher the value of the coefficient of permeability. Here 'e' is the void ratio. Based on other concepts it has been established that the permeability of a soil varies as e 2 or e 3 /(1+e). Whatever may be the exact .Falling Head Test Calculations. Permeability Falling Head (K) = 2.303 . Soils of low permeability require flow under a high head for periods ranging from a day to a week depending upon the permeability and the head. Alternatively, in the .
The porosity and permeability calculator uses Darcy's law to calculate these two material properties as fluids flow through porous substances. . 1 to 10 darcy, depending on soil type. A very sandy soil will be more permeable (~10 .
typical permeability of soils
Soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. Texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter influence the permeability. 9.8: Soil Permeability - Geosciences LibreTextsVariable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. . Calculations 7 Mass of soil = (2) – (1) 8 Bulk Density = mass/volume 9 Dry density (Pd)= P/(1+W) 10 Void .
Determination of permeability of the soil is significant implement of the test to estimate ground water flow, to calculate seepage through dams and settlement of structure and also significant in environmental conditions, in the current methods of determining the permeability carried out in situ and requires various test mostly in routine .Permeability Test. 9. Direct Shear Test. 10. Triaxial Test. 11. Unconfined Compressive Strength Test. 12. . When a load is applied to a low permeability soil, it is initially carried by the water that exists in the porous saturated soil and result in a rapid increase of pore water pressure. . Calculate the void ratio at the end of primary . In this soil permeability test, the differential pressure (the head) through the sample is allowed to decrease as water infiltrates the sample. Thus, there is diminishing pressure over the course of the test. . Simple Field Percolation Test – measuring the rate of drop in water level in an accurately sized hole enables calculation of . The purpose of this test is to determine the permeability (hydraulic conductivity) of a sandy soil by the constant head test method. There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: The constant head test method, and (2) the falling head test method. The constant head test method is used .
Correspondingly, the calculation formula for air permeability in soils is derived based on the test equipment and test principle, mainly regarding air permeability K a and coefficient of air permeability k a. According to the test environment, the test equipment can be divided into two types: field-type and laboratory-type. The higher a material's permeability, the easier it will be for a fluid to flow through it. Permeability depends on whether the pores are or are not connected and as well as the size of the pores. To calculate permeability, we use Darcy's law. This equation describes the flow of a fluid (gas or liquid) through a porous medium (rocks, soil .PERMEABILITY TEST METHOD A. SCOPE. The permeability test is a measure of the rate of the flow of water through soil. In this test, water is forced by a known constant pressure through a soil specimen of known dimensions and the rate of flow is determined. This test is used primarily to. determine the suitability of sands and gravels
FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is definedThe results of sieve analyses, plotted in the form of a gradation curve, are used to estimate soil permeability. The following tests shall be performed on samples obtained to verify the field . the soil sample. The testing will be accompanied by means of a hydrometer analyses. The . The formula used to calculate the group index is as .

snopes bottled water test
11 de jan. de 2024 · loira cavala sentando. chinafrpmould.com 2024-01-11 11:12:58 4752. bucetinha bronzeada. madrasta bbw. chinafrpmould.com 2024-01-11 01 . morena cavala peituda. morena cavala peituda. chinafrpmould.com 2024-01-11 08:25:24 5153. morena peituda cavala. morena peituda cavala. chinafrpmould.com 2024-01-10 22:33:16 7283. .
soil permeability test calculation|permeability of soils chart